Introduction
This blog will introduce you to Bluetooth Low Energy and will cover all the end-use application areas where it is used. Furthermore, the blog will also walk you through different kinds of BLE beacons and popular beacon protocols.
In the latter half of the article, we will create a demo android application to test out 2 BLE Beacon protocol, one from Apple and one from Google. But, let us first go through some basic definitions and an overview of BLE and Beacons before jumping onto the coding part.
Bluetooth Low Energy
Bluetooth Low Energy is a wireless personal area network technology designed by Bluetooth SIG. The Bluetooth SIG identifies different markets for low energy technology, particularly in the field of smart home, health, sport, and fitness sectors. Some of the key advantages include:
- low power requirements can run for months/years on a button cell
- small size and low cost
- compatibility with mobile phones, tablets, and computers
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), available from Android API 18(4.3 — Jelly Bean), and later creates short connections between devices to transfer bursts of data. BLE when not connected it remains in sleep mode. This is because as compared to Classic Bluetooth it utilizes less power by providing lower bandwidth. It is ideal for applications such as a heart-rate monitor or a wireless keyboard. To use BLE, devices need to have a chipset that supports BLE. Talking about BLE Beacons, Bluetooth Beacons are physical transmitters – a class of BLE devices that broadcast their identifiers on nearby electronic devices.
Use Cases of BLE Beacons
These beacons can be used for many proximity-related applications such as –
- Proximity Alerts: These beacons can be used to get alerts in-app when they are in the vicinity
- Indoor Navigation/ Location: By using a proper number of beacons placed in the room and utilizing the signal strength of all the beacons properly, we can create a working solution for indoor navigation or indoor location.
- Interactions: These beacons can be placed on the poster/banner of a movie in a movie theatre and as soon as the device comes in proximity of it app can launch its trailer or teaser, the same can be done for museums where these can be placed on the art piece and people can the details of these painting as notification and also get video/audio/text info for the art piece.
- Healthcare: it can be used for tracking patient movement and activities
It can be used for many other use cases as well. For instance, you can place a BLE tag in your key and then can use your mobile phone to search for it if it’s inside a cupboard or just lying under the sofa.
Beacon Protocols
- iBeacon: Apple’s standard for Bluetooth beacon
- AltBeacon: It is an open-source alternative to iBeacon created by Radius Networks
- URIBeacon: It directly broadcast URL which can be understood immediately
- Eddystone: Google’s standard for Bluetooth beacons, It supports three types of packets, Eddystone-UID, Eddystone-URL, and Eddystone-TLM.
Now, we will see how we can scan for Apple’s iBeacon and Google’s Eddystone-UID by creating a demo android application.
Getting Started
Create a new project and choose the template of your choice.
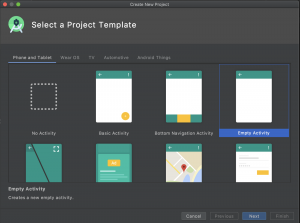
I chose “Empty Activity”.
BLE Dependency
There is no extra BLE library dependency as such for scanning for BLE beacons.
Open AndroidManifest.xml and add the following in the manifest element.
<uses-feature> tag with required as “true” means that this app requires BLE hardware to work with hence Google play will make sure that this app is only visible to devices that have the BLE hardware Available.
<uses-permission> tag is required to get the permission to use the Bluetooth hardware with Coarse location in Low energy mode.
Check for Permission
Coarse location permission is needed for Bluetooth low energy scanning mode. Hence we should make sure that we have the required permission provided by the user.
Check whether got the permission else to show the dialog letting the user know why we need this permission.
Setting up Bluetooth API
Initialize the BluetoothManager to get the instance of BluetoothAdapter for getting BluetoothLeScanner, which is required to perform scan related operations for Bluetooth LE devices.
- BluetoothManager: High-level manager used to obtain an instance of a BluetoothAdapter and to conduct overall Bluetooth Management.
- BluetoothAdapter: Represents the local device Bluetooth adapter. The BluetoothAdapter lets you perform fundamental Bluetooth tasks, such as initiate device discovery, query a list of bonded (paired) devices, instantiate a BluetoothDevice using a known MAC address, and create BluetoothServerSocket to listen for connection requests from other devices and start a scan for Bluetooth LE devices.
- BluetoothLeScanner: This class provides methods to perform scan related operations for Bluetooth LE devices.
BLE Scan Callbacks
BLE Start/Stop Scanner
We can have the button to control the start and stop of the BLE scanner.
Parse ScanResult to Get Relevant Data
We should create a Beacon class to hold the different info we will be parsing from ScanResult from onScanResult callback.
Extracting Eddystone UID packet info if there is any.
Eddystone UID: A unique, static ID with a 10-byte Namespace component and a 6-byte Instance component.
- scanRecord: a combination of advertisement and scan response
- device.address: hardware address of this Bluetooth device. For example, “00:11:22:AA:BB:CC”.
- rssi: received signal strength in dBm. The valid range is [-127, 126].
- serviceUuids: list of service UUIDs within the advertisement that are used to identify the Bluetooth GATT services.
- eddystoneServiceId : Service UUID for Eddystone UID which is “0000FEAA-0000–1000–8000–00805F9B34FB”
- serviceData: the service data byte array associated with the serviceUuid, in our case eddystoneServiceId
- eddystoneUID packet info is there in serviceData from index 2 to 18, we need to convert this byte array to Hex string using the utility method.
- namespace is of 10 bytes which are starting 20 characters of eddystoneUID
- instanceId is of 6 bytes which are the remaining 12 characters of eddystoneUID
Extracting iBeacon packet info if there is any.
iBeacon: A unique, static ID with a 16-byte Proximity UUID component and a 2-byte Major component, and a 2-byte Minor component.
- iBeaconManufactureData: the manufacturer specific data associated with the manufacturer id, for iBeacon manufacturer id is “0X004c” (Apple).
- iBeacon UUID or Proximity UUID is of 16 bytes and extracted from iBeaconManufactureData from index 2 to 18, we need to convert this byte array to Hex string using the utility method
- major is of 2 bytes, range between 1 and 65535 and extracted from iBeaconManufactureData from index 18 to 20, we need to convert this byte array to Hex string using the utility method and then convert it to Integer
- minor is of 2 bytes, range between 1 and 65535 and extracted from iBeaconManufactureData from index 20 to 22, we need to convert this byte array to Hex string using the utility method and then convert it to Integer
Let’s see the code in Action
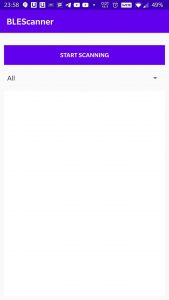
Figure- Start screen
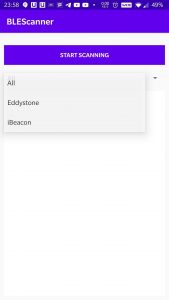
Figure- Start screen with the options
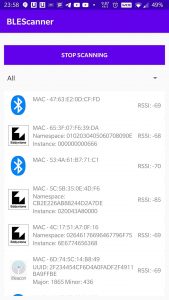
Figure- Result screen with Eddystone UID, iBeacon, generic BLE devices
BLE beacons iBeacon and Eddystone-UID are different from each other, however can be used for any of the proximity-related applications. It is because, at the application level, both of them solve similar problems using different Bluetooth profiles.
Eddystone do have a different type of packets to solve a different problem like-
- Eddystone-URL : for broadcasting URL
- Eddystone-TLM: broadcasts information about the beacon. This can include battery level, sensor data, battery voltage, beacon temperature, number of packets sent since the last startup, and beacon uptime, or other relevant information to beacon administrators
For more details and an in-depth view, you can find the code here









